Yes! Data analytics is a great career option due to its high demand, competitive salaries, and diverse opportunities across industries. It offers stability, career growth, and the chance to work with data-driven decision-making.
Key Benefits:
- High Demand – Companies rely on data to make informed decisions, creating a constant need for skilled analysts.
- Good Salary Potential – Competitive pay, especially with experience and specialized skills.
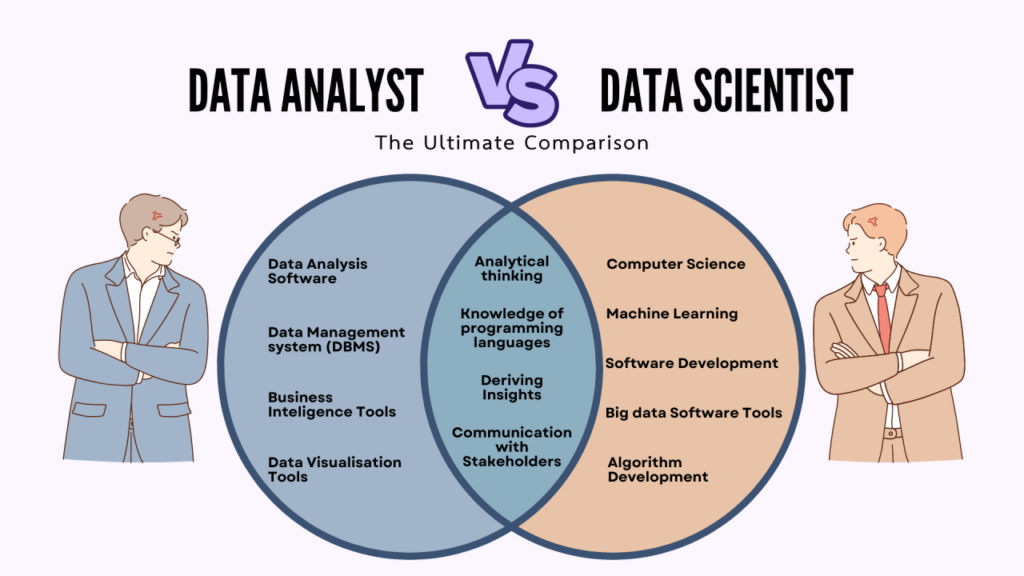
- Variety of Roles – Career paths include business intelligence, data science, marketing analytics, and more.
- Impactful Work – Your insights help businesses make smarter decisions.
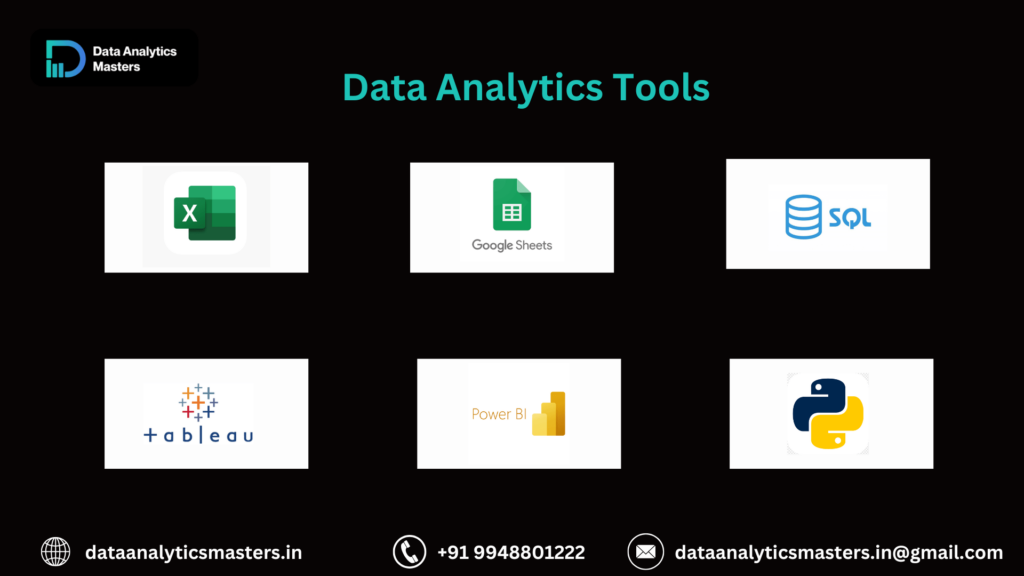
- Skill Development – Learning SQL, Python, and data visualization opens doors to various industries.






 in Hyderabad by Brolly.Group
in Hyderabad by Brolly.Group